SCOOP – Computer Science for Supply Chain OptimizatiOn Problems

Principal investigator: Eduardo García Pardo y Jesús Sánchez-Oro Calvo Funding entities: Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (PID2021-125709OA-C22). Duration: 2022 – 2024.
Summary:
This scientific proposal focuses on solving hard optimization problems belonging to the supply chain management, by using an efficient combination of Operations Research and Artificial Intelligence techniques. The Supply Chain refers to the series of resources, activities, and organizations that move materials and products through, on their journey from initial suppliers to final customers. The Supply Chain is the core of the operations that take place in industry.
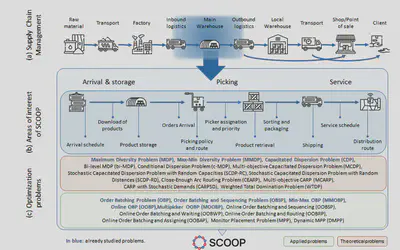
Particularly, we center our attention in the processes and systems related to warehouses, including the inbound and outbound logistics. The optimization of the processes within this context might suppose a large reduction of the costs and therefore an increase in the profits. Specifically, in this project, we propose the study of four families of optimization problems:
Order Batching: this family of problems is focused on the activities related to the picking of orders in a warehouse when the picking policy follows an order batching strategy (i.e., several orders are grouped into a batch before starting the picking route). Many optimization problems are classified under this family: offline (i.e., static)/online (i.e., dynamic); single-picker/multiple-pickers; minimizing different objective functions (time, route length, working balance, costs, etc.).
Routing: these problems hold a central place in the supply chain. In this family we can find node routing problems (simply called vehicle routing problems) in which customers can be represented by nodes in a network; and arc routing problems, in which the service is performed on the arcs or edges of a network. In this project, we target three realistic variants of routing problems that appear in the context of supply chain management: close-enough, stochastic, and multi-objective routing models.
Monitoring: networks are, an essential part of every activity in professional scenarios. In the supply chain, there are several networks whose security must be guaranteed such as: communication networks, transportation networks or surveillance networks. In this context, many optimization problems appear such as: selecting a number of points that maximize an area under surveillance, determining which network connections must be reinforced, or choosing which warehouses dominate/supply others.
Storage and location: in this research line, we are interested in both, studying the location of warehouses (within the strategic decision of a company) and also studying the right location of the products within the warehouse (from a tactical point of view). These applications can be modeled as, the so-called, capacitated and generalized dispersion problems (CDP).
To solve the aforementioned optimization problems, we will make use of heuristic and metaheuristic procedures. Belonging to the Artificial Intelligence field, those techniques are able to provide high-quality approximate solutions (some times even optimal) in short computing times. These techniques are suitable for tackling hard optimization tasks in real scenarios where the quality of the solutions is almost as important as the time needed to find them.
This project is built upon the strong and successful collaboration of the two complementary research groups involved in this proposal: mathematicians (Univ. de Valencia) coordinated by Profs. Martí and Martínez-Gavara, and computer scientists (Univ. Rey Juan Carlos) coordinated by Profs. Pardo and Sanchez-Oro